Seismic preparation for nuclear plants: Lowering costs without compromising safety
Rethinking seismic design may be key for making nuclear plant construction affordable.
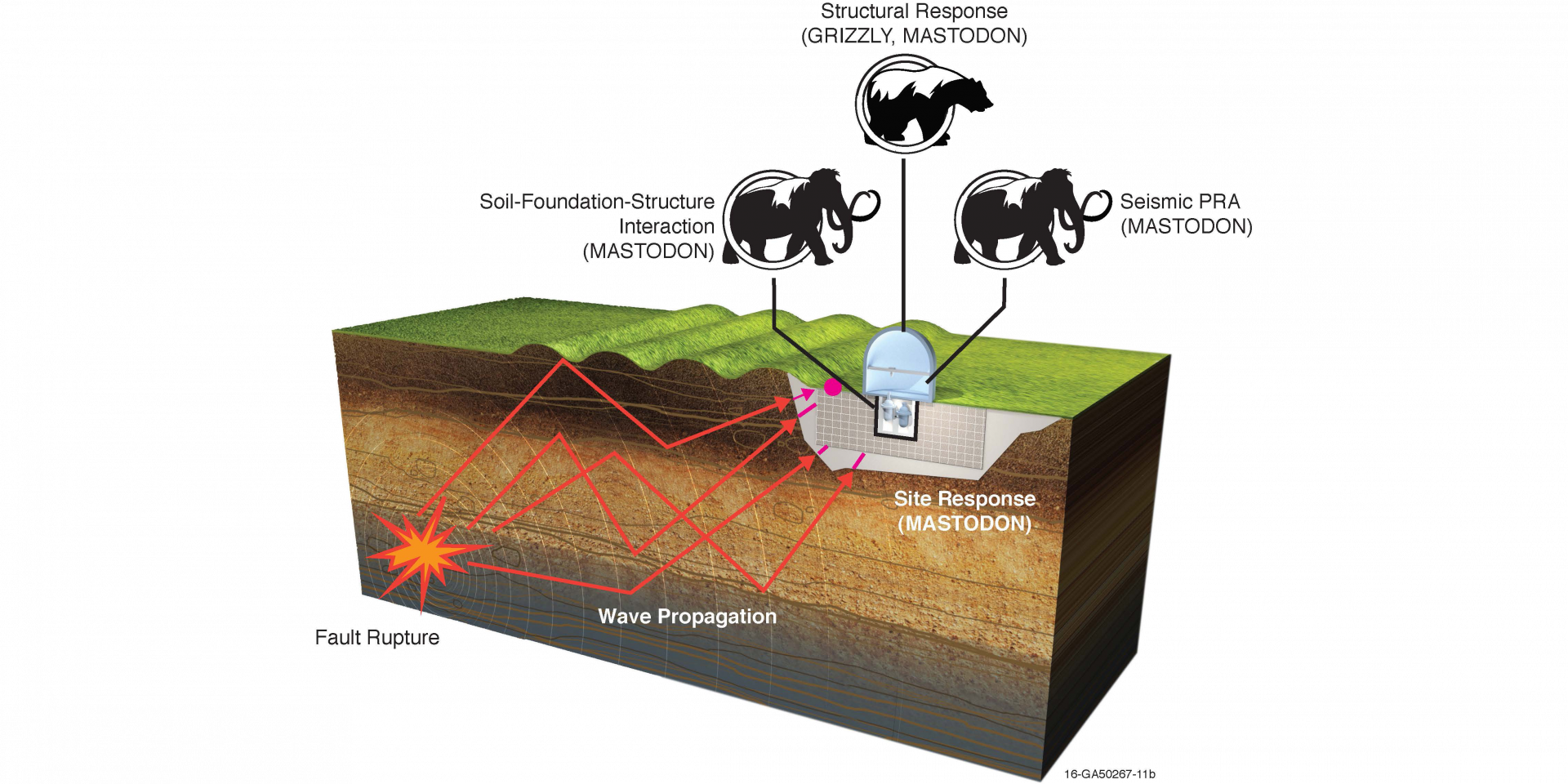
Nuclear power plants not only provide the nation’s largest source of carbon-free electricity, they also can operate 24 hours a day, 365 days a year to augment intermittent renewables such as wind and solar. Further, studies show that nuclear energy is among the safest forms of energy production, especially when considering factors such as industrial accidents and disease associated with fossil fuel emissions. All said, nuclear has the potential to play a key role in the world’s energy future. Before nuclear can realize that potential, however, researchers and industry must overcome one big challenge: cost.
A team at Idaho National Laboratory is collaborating with experts around the nation to tackle a major piece of the infrastructure equation: earthquake resilience. INL’s Facility Risk Group is taking a multipronged approach to reduce the amount of concrete, rebar, and other infrastructure needed to improve the seismic safety of advanced reactors while also substantially reducing capital costs. The effort is part of a collaboration between INL, industry, the Department of Energy’s Advanced Research Projects Agency–Energy (ARPA-E), and the State University of New York–Buffalo (SUNY Buffalo).



